Company: Google
Founded: 1996
Founders: Larry Page and Sergey Brin
Description: Technology company focused on internet search, email, advertising, AI, cloud computing and more.
This playbook focuses on marketing strategies and tactics used by Google.
The marketing playbook series is for founders who want to:
1. learn from real-life examples
2. discover which growth strategies fit which businesses and industries
3. find the 20% of strategies that return 80% of results
- Freemium Marketing
- Partnership Marketing
- Flywheel Marketing
- 8. Google Search
- 9. Android
- 10. G Suite (Gmail, Docs, Sheets, Slides, Hangout, etc)
- 11. Google Chrome
- 12. Google + YouTube
- 13. Google Maps
- 14. Google Ads
- 15. Google Fi
- 16. Google Hardware
- 17. CapitalG (formerly Google Capital)
- 18. Google+ (Shutdown)
- 19. Google AI
- 20. Google X (Moonshot Factory)
- 21. Google Cloud Platform
- 22. Google Fiber
- Remarkable Marketing
- Personalized Marketing
- Gamified Marketing
- Language Marketing
- Habit Marketing
- Piggyback Marketing
Freemium Marketing
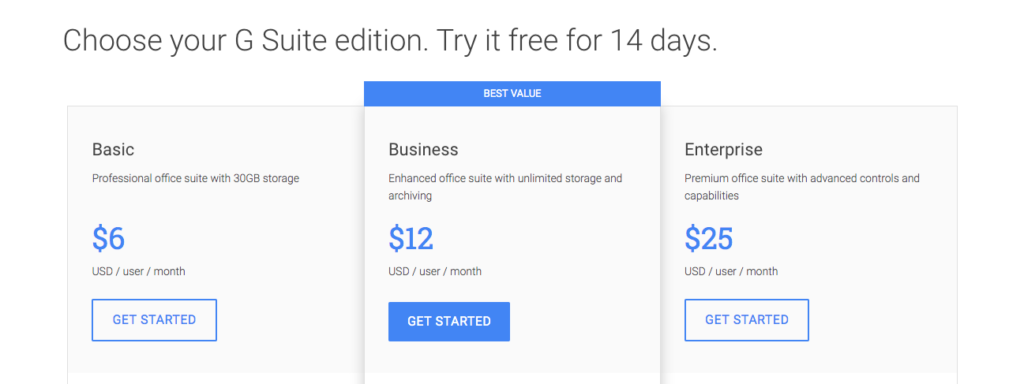
1. G Suite
Gmail is free for personal use but costs for businesses. Many business owners go with G Suite because they’re already familiar with the interface and trust the brand. (Pricing)

2. AdWords Credit
Google urges new businesses to start advertising with AdWords credit. (Article)

3. YouTube Premium
Most of us use YouTube for free but they offer a paid version with enhanced features. (Pricing)
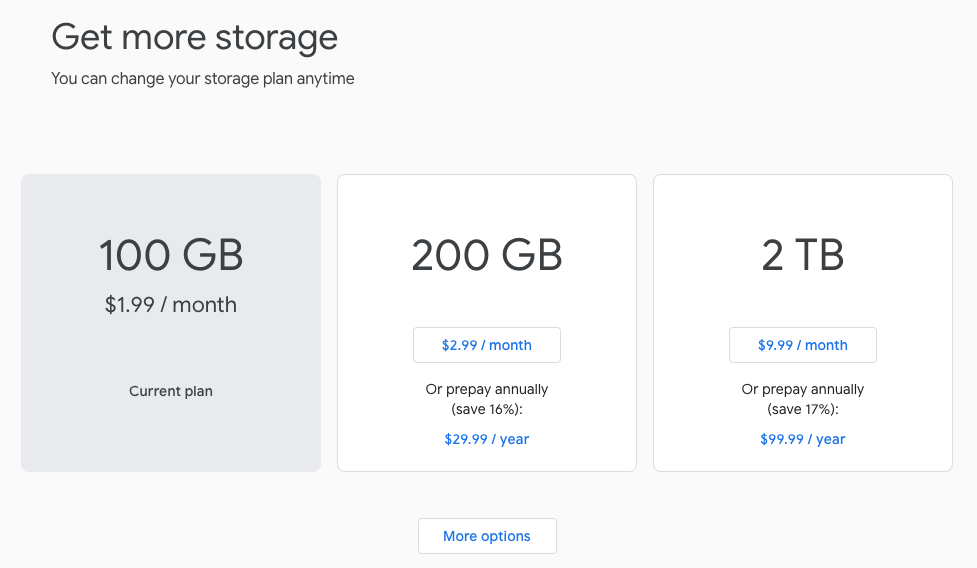
4. Google Drive
Google users who exceed free storage limits will be prompted to pay for additional storage space. (Pricing)
Partnership Marketing

5. YouTube + Samsung
YouTube and Samsung partnered to offer 4 months of YouTube Premium to new Samsung Galaxy owners. (Article)

6. Google Ads + Squarespace
Squarespace and Google partnered to offer $100 AdWords credit to new Google Ads customers. (Post)

7. Samsung Chromebook
Google and Samsung partnered to create a line of Chromebooks. (Article)
Flywheel Marketing

8. Google Search
Google followed up on it’s first big success with additional products such as Books, Shopping, News, Images, Flights, Reviews, Alerts and Finance.
Google Search users often complain about missing some combination of these features when they switch to new search engines. Competitors may find themselves recreating several products just to reach feature parity. (Wiki)

9. Android
Google made a major move into mobile with the purchase of Android. It now serves as a central force for other products such as Google Pay, Play Store, YouTube, Google Maps, and Google Fi.
Android also gave Google a presence beyond phones. Developers use Android on watches, TVs, cars and more. (Page)
10. G Suite (Gmail, Docs, Sheets, Slides, Hangout, etc)
Google turned the success of Gmail into G Suite. G Suite products such as Google Docs and Google Sheets have become formidable competitors in office software space. (Article)

11. Google Chrome
Google also came to dominate the browser market with Chrome. Chrome complements other products such as Search, Analytics, Ads and Lighthouse. (Discussion)

12. Google + YouTube
Google tried to compete with YouTube before purchasing the competitor. Since then YouTube has become the second most visited site in the US, only second to Google itself. (Wiki)
13. Google Maps
Google Maps is used by millions of people and powers thousands of apps via API. It complements other products such as Streets View, Google Earth, Google Translate and Waze. (Wiki)

14. Google Ads
Ads and search-level targeting is what made Google a billion dollar behemoth. Experience in ads allowed Google take advantage of opportunities from other products such as Analytics and YouTube. (Page)

15. Google Fi
With the Android operating system and hardware in place, Google became a carrier. Customer acquisition costs for Google Fi may be lower than other carriers with pre-existing relationships from it’s other products. (Page)

16. Google Hardware
Google moved from the software space into the competitive hardware space with products such as the Chomebook, Pixelbook, Google Home, Google Pixel, Chromecast, Stadia and Nest.
Many of these products run on Android OS, with Google Assistant and apps from the Play Store. (Page)

17. CapitalG (formerly Google Capital)
Google also leverages the efforts (and speed) of others by investing in startups. Some Google investments include Airbnb, Uber, Glassdoor and Thumbtack. (Page)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/google-plus-57d9e4d53df78c9cceedc5e1.png)
18. Google+ (Shutdown)
Some attempts at flywheel marketing will fail. Projects such as Google+, Google Reader, Google Glass and Google Offers were shutdown for suboptimal performance but show a commitment to using product combinations to dominate markets. (Article)

19. Google AI
Google recently rebranded itself as an AI company. This makes sense with the data it has from it’s web of products.
Other AI products include DeepMind, Waymo, Kaggle, Google Assistant and TensorFlow. (Article)

20. Google X (Moonshot Factory)
Google/Alphabet dedicated an entire portfolio company to experimentation. They have already spun off multiple companies including Malta, Dandelion and Makani. (Projects)

21. Google Cloud Platform
Google runs one of the most server-intensive businesses in the world. They are well-positioned to offer cloud services to developers. Google Cloud Platform is complemented by other products such as Maps API, Dart, Go, Firebase, Google Domains, Google CDN and Google Fonts. (Page)

22. Google Fiber
Google Fiber was another move into the physical world. Since Fiber, Google has followed up with projects such as Sidewalk Labs. (Page)
Remarkable Marketing

23. Google Art & Culture App
Google’s Art and Culture app went viral as we rushed to find out which art pieces matched our selfies. (Article)

24. Google Assistant Booking Appointments
A demo of Google’s assistant got lots of press when it booked a hair appointment without the receptionist noticing that it wasn’t a real person. (Video)

25. Google Doodles
Google Doodles spark lots of online discussion whenever the default logo is dropped for another theme. (Archive)
Personalized Marketing

26. Custom Search Results
Google uses search activity and location to personalize search results. Personalization makes it more difficult for other engines to compete without data on which results you prefer. (Wiki)

27. Video Recommendations
Google-owned YouTube also offers personal recommendations. YouTube recommendations aim to extend time spent on YouTube.
YouTube’s focus on retention has led to some pretty funny memes on the clickbait that gets surfaced. (Article)
Gamified Marketing

28. Doodle Contests
Google Doodle contests attract artists and their networks to the search engine. (Page)

29. Kaggle Contests
Google-owned Kaggle uses contests to attract talent and solve business problems at a fraction of the cost of hiring. (List)
Language Marketing

30. Google – Verb
Google is one of the few brands that has worked it’s way into the English language. They receive free mind share as we express ourselves. (Definition)
Habit Marketing

31. Internet Usage
Google benefits from our insatiable curiosity and mindless addiction to screens. (Post | Article)

32. YouTube
Many of people use YouTube to escape. Combined with push notifications, recommendations and autoplay, no wonder why YouTube is the second-most visited site in the US. Second to Google. (Article)

33. Gmail
Boredom, badges and push notifications prompt us to mindlessly check our email. (Article)
Piggyback Marketing

34. Google Fiber Shirts
Google Fiber sent free shirts to residents of cities where the service is available. In turn, residents raise brand awareness, display support and activate social proof. (Tweet)

35. Subscribe to us on YouTube
YouTube content creators promote the platform by soliciting subscriptions. Twitter and Instagram have the same dynamic of users promoting the platform. (Article)

36. Review Us on Google
Businesses are promoting for Google by soliciting customer reviews. (Page)

37. @gmail.com
Gmail users seamlessly promote the platform by sending email. (Article)

38. Google Identity Platform
Google gets prominent placement on other sites by offering third-party authentication. This also keeps users signed into Google accounts. (Page)

39. Google Play
Developers promote Google Play whenever they encourage users to download their apps. (Page)

40. Google Assistant Actions
External companies are making Google Assistant more powerful and giving their customers reasons to try the service. (Page)
Thanks for reading!
Which company you would like to see next?
Let me know — @DruRly.
Check out the playbook series for more growth strategies.